Scapular stabilization is the process of strengthening muscles that anchor and control the shoulder blades, essential for proper shoulder function, posture, and injury prevention.
1.1 What is Scapular Stabilization?
Scapular stabilization refers to the process of controlling and anchoring the shoulder blades (scapulae) to ensure proper movement and alignment of the shoulder joint. It involves strengthening the muscles that support the scapula, such as the serratus anterior and trapezius, to enhance posture, mobility, and overall shoulder function. Effective stabilization prevents misalignment and promotes efficient movement patterns, reducing the risk of injury and improving athletic performance.
1.2 Importance of Scapular Stabilization
Scapular stabilization is crucial for maintaining proper posture, preventing shoulder injuries, and enhancing overall shoulder function. It strengthens key muscles like the serratus anterior and trapezius, ensuring the scapula moves efficiently during arm movements. Proper stabilization reduces the risk of conditions like shoulder impingement and improves athletic performance by promoting optimal movement patterns and reducing strain on the shoulder joint.

Benefits of Scapular Stabilization Exercises
Scapular stabilization exercises improve posture, enhance shoulder mobility, and prevent injuries by strengthening stabilizer muscles, reducing strain during physical activities, and promoting overall shoulder health and stability.
2.1 Improved Posture
Scapular stabilization exercises strengthen the muscles that support the shoulder blades, improving posture by reducing rounded shoulders and promoting proper spinal alignment. This reduces the strain on the upper back and neck, enhancing overall comfort and reducing the risk of postural-related discomfort and injuries.
2.2 Enhanced Shoulder Mobility
Scapular stabilization exercises enhance shoulder mobility by improving the coordination and strength of the muscles surrounding the shoulder blades. This allows for a fuller range of motion, reduces stiffness, and ensures smooth, controlled movements. Better mobility also supports everyday activities and athletic performance, making it easier to perform overhead movements and other dynamic actions with confidence and precision.
2.3 Injury Prevention
Scapular stabilization exercises play a crucial role in injury prevention by strengthening the muscles that support the shoulder blades. This enhanced stability reduces the risk of shoulder injuries, particularly in overhead athletes and individuals with poor posture. Stronger scapular muscles help absorb and distribute forces more effectively, minimizing strain on the shoulder joint and surrounding tissues during physical activity.

Key Principles of Scapular Stabilization Exercises
Scapular stabilization exercises focus on proper technique, consistent practice, and gradual progression to build strength and stability in the shoulder muscles, enhancing overall shoulder function and health.
3.1 Proper Technique
Proper technique is vital for effective scapular stabilization exercises. This includes maintaining neutral spine alignment, engaging core muscles, and ensuring controlled movements. Avoid rounding shoulders or using momentum, as this can lead to poor form and reduced effectiveness. Focus on slow, deliberate actions to maximize muscle activation and minimize risk of injury or strain.
3.2 Frequency and Duration
Perform scapular stabilization exercises 3-4 times weekly for optimal results. Each session should last 20-30 minutes, incorporating 2-3 sets of 12-20 repetitions per exercise. Consistency is key to building strength and stability. Adjust frequency and duration based on fitness level, ensuring adequate rest to prevent overtraining and promote muscle recovery.
3.4 Progression of Exercises
Progress exercises by increasing resistance, intensity, or complexity as strength improves. Start with basic drills like scapular squeezes, then move to dynamic movements such as wall slides or resistance band exercises. Advanced options include single-arm rows and incline serratus punches. Gradual progression ensures continued improvement and prevents plateaus, while maintaining proper form is crucial to avoid injury.
Scapular Stabilization Exercises
Scapular stabilization exercises, such as scapular squeezes and wall slides, target the muscles around the shoulder blades to enhance strength, posture, and mobility effectively with minimal equipment.
4.1 Scapular Squeeze
The scapular squeeze is a simple yet effective exercise that involves squeezing the shoulder blades together while maintaining proper posture. It targets the rhomboids and trapezius muscles, improving scapular stability and strength. To perform, sit or stand tall, engage the core, and pull the shoulders back without arching the spine. Hold for 5 seconds, then release. This exercise enhances posture, reduces shoulder tension, and promotes proper shoulder mechanics, making it a foundational movement for scapular health.
4.2 Wall Slides
Wall slides are an excellent exercise for improving scapular mobility and stability. Stand facing a wall with hands at shoulder height. Slowly slide arms upward, keeping palms on the wall, and squeeze shoulder blades together as arms reach overhead. Lower arms to the starting position and repeat. This exercise enhances scapular control, reduces shoulder strain, and promotes proper posture, making it ideal for individuals with shoulder mobility issues.
4.3 Resistance Band Exercises
Resistance band exercises are versatile tools for enhancing scapular stability. They provide continuous tension, activating stabilizer muscles like the serratus anterior and rhomboids. Common exercises include banded rows, presses, and rotations. These movements strengthen the scapula, improve posture, and reduce injury risk. Use light to medium resistance and focus on controlled movements to maximize effectiveness and maintain proper form throughout each exercise.
4.4 Stability Ball Push-Ups
Stability ball push-ups challenge the scapular stabilizers by requiring controlled movement on an unstable surface. Start with hands on the ball and lower your chest, keeping elbows close. This exercise engages the serratus anterior and triceps, improving scapular strength and stability. Perform 8-12 reps, focusing on maintaining a rigid core and avoiding shoulder shrugging to ensure proper form and effectiveness.
4.5 Prone Rows
Prone rows are an effective exercise for scapular stabilization, targeting the rhomboids and trapezius muscles. Lie on your stomach with arms extended, lift your chest slightly, and pull your arms toward your sides, squeezing your shoulder blades together. This exercise strengthens the muscles that stabilize the scapula, improving posture and reducing the risk of shoulder injuries. Perform 8-12 reps for optimal results.

Advanced Scapular Stabilization Exercises
Advanced exercises like single-arm rows and scapular push-ups challenge the stabilizer muscles, enhancing strength and control. They are ideal for those with a solid foundation in basic stabilization techniques.
5.1 Single-Arm Rows
Single-arm rows target the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and rhomboid muscles, enhancing scapular stability and strength. Perform with a neutral spine, pulling the weight toward your hip, and controlling the movement. This exercise improves balance, reduces muscle imbalances, and enhances overall shoulder function; It’s ideal for advanced individuals seeking to challenge their scapular stabilizers effectively.
5.2 Scapular Push-Ups
Scapular push-ups are advanced exercises that target the scapular stabilizers, including the serratus anterior and trapezius muscles. Performed in a plank position, they involve maintaining a straight line from head to heels while moving the scapula forward and backward. This exercise enhances dynamic scapular control, improves shoulder stability, and is ideal for individuals with a strong foundation in scapular stabilization techniques.
5.3 Incline Serratus Punch
The incline serratus punch is an advanced exercise targeting the serratus anterior, crucial for scapular stabilization. Performed on an incline bench, it involves punching forward with light weights while maintaining scapular control. This movement enhances scapular protraction and improves shoulder mobility, making it effective for athletes seeking to enhance their overhead performance and overall shoulder stability.
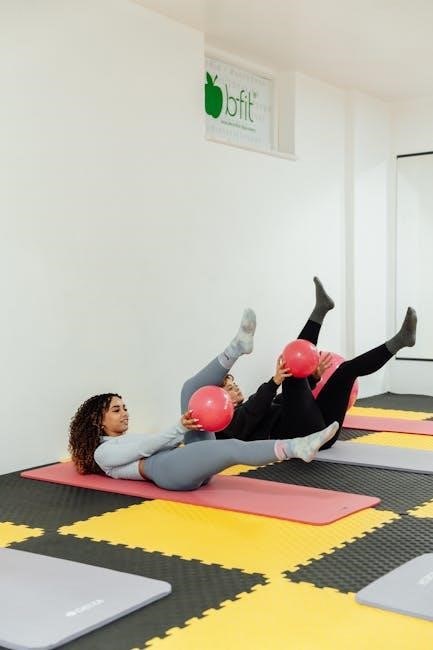

Sample Exercise Routine
A well-structured routine includes a warm-up, core exercises, and a cool down. Perform scapular squeezes, wall slides, and resistance band exercises 3-4 times weekly for 20-30 minutes.
6.1 Warm-Up
A proper warm-up prepares the muscles for scapular stabilization exercises. Begin with 5-10 minutes of dynamic stretches, such as arm circles, shoulder rolls, and light cardio like jogging in place. Incorporate gentle movements to increase blood flow and flexibility in the shoulder and upper back region. This helps prevent injury and enhances the effectiveness of subsequent exercises.
6.2 Core Exercises
Strengthening the core is vital for scapular stabilization, as it provides a stable base for shoulder movements. Incorporate exercises like planks, bird-dog, and pelvic tilts to enhance trunk stability. These exercises improve balance, posture, and overall upper body control, ensuring efficient transfer of force during movements. Consistent core work supports long-term scapular health and athletic performance.
6.3 Cool Down
A proper cool-down after scapular exercises involves gentle stretches and foam rolling to relax muscles. Focus on the shoulders, chest, and upper back to reduce tension and improve flexibility. Deep breathing and static stretches, such as child’s pose or cat-cow, promote recovery and maintain mobility. A well-structured cool-down enhances overall muscle balance and prevents post-exercise stiffness.
Role of Scapular Stabilization in Injury Prevention
Scapular stabilization strengthens shoulder muscles, reducing injury risk by improving posture, mobility, and joint stability, essential for athletes and individuals with repetitive shoulder movements.
7.1 Common Injuries Related to Poor Scapular Stability
Poor scapular stability often leads to injuries like rotator cuff strains, shoulder impingement, and scapular winging. These issues arise from weakened muscles, leading to improper shoulder mechanics and pain during overhead movements or repetitive activities. Strengthening exercises can help prevent these injuries by improving muscle control and maintaining proper shoulder alignment during daily and athletic activities.
7.2 Preventative Measures
Regular scapular stabilization exercises, such as scapular squeezes and wall slides, can prevent injuries by strengthening the muscles around the shoulder blades. Proper posture, ergonomic adjustments, and incorporating these exercises into daily routines help maintain shoulder health and reduce the risk of developing conditions like rotator cuff strains or shoulder impingement.

Scapular Stabilization and Rehabilitation
Scapular stabilization is crucial in rehabilitation, helping restore strength and function after injuries or surgeries. It ensures proper shoulder mechanics and prevents further strain during recovery.
8.1 Post-Injury Rehabilitation
Post-injury rehabilitation focuses on restoring scapular strength and stability to facilitate recovery. Gentle exercises like scapular squeezes and wall slides are often used to improve muscle activation and proper movement patterns, reducing pain and preventing future injuries while promoting functional recovery of the shoulder complex.
8.2 Surgical Recovery
Following surgery, scapular stabilization exercises are crucial for restoring strength and mobility. Gentle exercises like wall slides and scapular squeezes help promote healing, maintain proper alignment, and prevent complications. These exercises are tailored to support the recovery process, ensuring the shoulder complex regains stability and function effectively after surgical intervention.
Scapular stabilization exercises are essential for improving posture, preventing injuries, and enhancing shoulder function. They play a vital role in both fitness and rehabilitation, ensuring long-term shoulder health.
9.1 Summary of Key Points
Scapular stabilization exercises enhance posture, shoulder mobility, and injury prevention by strengthening key muscles like the serratus anterior and trapezius. They are effective for both fitness and rehabilitation, promoting long-term shoulder health and stability.
9.2 Final Thoughts
Incorporating scapular stabilization exercises into your routine is crucial for maintaining shoulder health, preventing injuries, and improving overall upper body strength. Consistency and proper technique are key to achieving long-term benefits and ensuring optimal shoulder function in both daily activities and athletic performance.

Additional Resources
Explore detailed guides, video tutorials, and expert articles online for comprehensive insights into scapular stabilization exercises, ensuring a well-rounded understanding and effective implementation of techniques.
10.1 Recommended Reading
Enhance your knowledge with books like “Scapular Strengthening Exercises” and “Shoulder Stability Workouts.” eBooks such as “Scapular Stabilization Protocols” and “Rotator Cuff & Scapular Strengthening Exercises” offer detailed routines. These resources provide expert guidance, step-by-step instructions, and scientific insights, helping you master scapular stabilization techniques effectively. They are available online and in sports therapy sections of libraries and bookstores.
10.2 Video Tutorials
YouTube offers a wealth of video tutorials on scapular stabilization exercises. Channels like Physiotherapy and Sports Rehab provide detailed demonstrations. Search for “scapular stabilization exercises” or “shoulder stability workouts” to find instructional content led by professionals. These videos guide you through exercises like wall slides and scapular squeezes, ensuring proper form and technique for effective results. They are perfect for visual learners seeking step-by-step instruction and expert advice.

Proper Form and Technique
Proper form and technique are crucial for effective scapular stabilization. Maintain a neutral spine, engage core muscles, and ensure controlled movements to avoid compensation and maximize results.
11.1 Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes include rounding shoulders, using momentum, and neglecting core engagement. These errors can reduce exercise effectiveness and increase injury risk. Ensure controlled movements, maintain proper posture, and focus on muscle activation to optimize results and prevent harm during scapular stabilization exercises.
11.2 Correcting Form
To correct form, focus on engaging core muscles and maintaining neutral spine. Pull shoulders back and down, avoiding shrugging. Use slow, controlled movements and ensure scapular engagement. Practice proper breathing to maintain stability and prevent compensatory patterns. Regular form checks and adjustments can enhance exercise effectiveness and reduce injury risk during scapular stabilization exercises.